Turbochargers
A turbocharger (turbo) is simply an air compressor
that is driven by a turbine using exhaust gases gas a
power source. Turbos create boost (higher intake air
pressure) without taxing the engine, thus its “free”
horsepower.
The downside of the turbocharger is that it takes time
for the engine to produce enough exhaust to spin the
turbine fast enough to create boost. This delay is
referred to as turbo lag. There are several methods
used to reduce turbo lag, and they include using two
turbos.
With two or twin turbos, one small turbo that spools
quickly, but, doesn't produce a lot of boost is
followed by a second larger turbo that spools slowly,
although it produces most of the boost. The idea
here is that the smaller quicker turbo produces just
enough boost to overcome most of the turbo lag
before the main turbo kicks in. The obvious
downside is that multiple turbos require more
complex plumbing and increase heat-which according
to combustion 101 is bad for horsepower.
that is driven by a turbine using exhaust gases gas a
power source. Turbos create boost (higher intake air
pressure) without taxing the engine, thus its “free”
horsepower.
The downside of the turbocharger is that it takes time
for the engine to produce enough exhaust to spin the
turbine fast enough to create boost. This delay is
referred to as turbo lag. There are several methods
used to reduce turbo lag, and they include using two
turbos.
With two or twin turbos, one small turbo that spools
quickly, but, doesn't produce a lot of boost is
followed by a second larger turbo that spools slowly,
although it produces most of the boost. The idea
here is that the smaller quicker turbo produces just
enough boost to overcome most of the turbo lag
before the main turbo kicks in. The obvious
downside is that multiple turbos require more
complex plumbing and increase heat-which according
to combustion 101 is bad for horsepower.
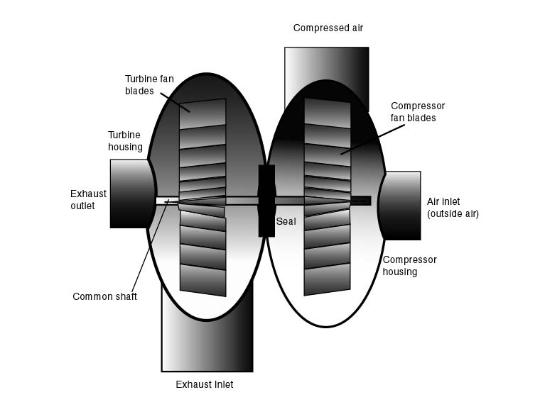
Turbocharger diagram

